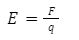
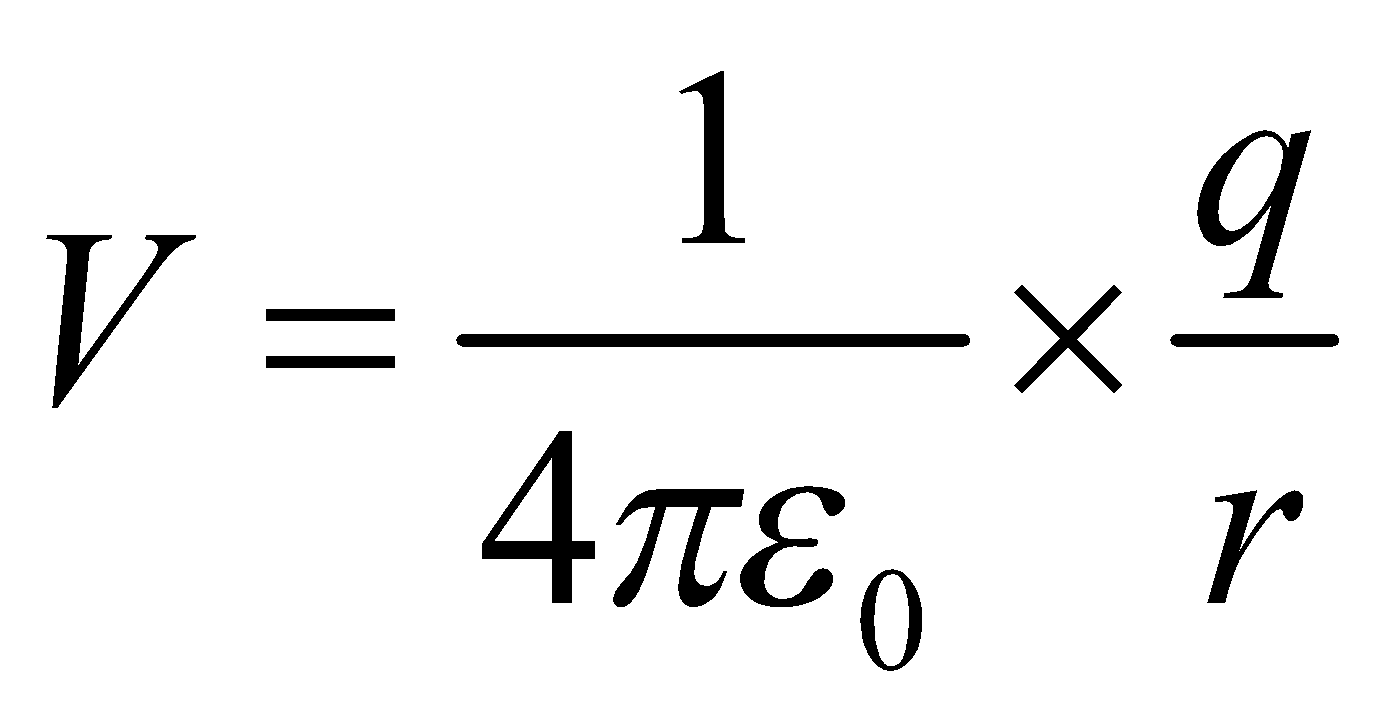
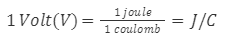
There are various properties of electricity that are expressed in different measurement units. However, we will learn about electric charge. Electric charge is one of the electrical properties. Electric charge is a physical property of matter causing it to experience a force when it is placed in an electromagnetic field. Electric charge is carried by subatomic particles and there are generally positive electric charges and negative electric charges.
Electric Charges
Electric charge is the fundamental physical property of matter because of which the matter experiences a force whenever it is kept in an electromagnetic field. Electric charge is also defined as the amount of energy or electrons which is transferred from one system or body to another system or body. This transfer of electrons happens through various processes such as conduction, induction, or certain specific methods.
Generally, there are two categories of electrical charges which are positive charges, carried by protons and negative charge is carried by electrons. If the total charge on a body is zero, that is neither positive nor negative, then it is said to be neutral. Electric charge is denoted as Q and measured in coulombs. The SI unit of charge is the coulomb.
Positively Charged Particles
In the positively charged particles, the number of positive ions is larger than the number of negative ions. In other words, the number of protons is larger or more than the number of electrons.
To make the positively charged particles neutral, electrons from the surroundings come to positively charged particles until the number of protons and electrons are equal.
Negatively Charged Particles
In negatively charged particles, the number of negative ions is larger than the number of positive ions. In other words, the number of electrons is larger than the number of protons.
To neutralize the negatively charged particles, as the protons cannot move and cannot reach the negatively charged particles, the electrons move towards another positively charged particle around them.
Neutral Particles
Neutral particles contain an equal number of protons and electrons. Neutral particles have all protons, neutrons and electrons but the number of positive ions (protons) are equal to the number of negative ions (electrons).
SI Unit of Electric Charge
The SI unit of electric charge is Coulomb, which is a derived SI unit and is denoted by C. One coulomb is the amount of charge which flows through an electrical conductor carrying one ampere per second.
In addition, the CGS unit of electric charge is given as a combination of three basic quantities such as mass, length and time.
Electric Field
The electric field in mathematical terms is defined as a vector field which can be associated or connected with each point in space. At that point, the force per unit charge is exerted on positive test charge which is at rest.
Electric field is generated by the electric charge or can be generated by time-varying magnetic fields.
Direction of Electric field
Direction of the field is the same as the direction of force which acted on a positive charge. The electric field is radially outwards from positive charge and inwards from negatively point charge.
Electric field intensity
The space around an electric charge where its influence is felt is termed as the electric field. The intensity of an electric field at a point is the force experienced by a unit positive charge which is placed at that point.
The intensity of an electric field is a vector quantity that has magnitude as well as direction.
Formula: ![]()
Unit: N/C or V/m
Electric Potential
Electric potential is defined as the amount of work needed to move one unit charge from a reference point to a particular or certain point against the electric field. When a body moves against the electric field, it gains a certain amount of energy, that energy is termed as the electric potential. The electrical potential of the charge is generated by dividing the potential energy with the amount of charge.
Electric potential formula
The electric potential formula is given as
![]()
Electric Potential Derivation
We will see the electric potential derivation due to point charge here.
Due to a Point Charge
The electric potential in an electric field at any point is the amount of work done needed to move a unit positive charge from infinity to that point along any path when electrostatic forces are applied.
Let us consider, a positive charge is placed at a point. The charge placed at that point will exert a force because the electric field is present.
The electric potential at any point with a distance of r from the positive charge q is given as,
![]()
Here,
V = Electric potential
q = test charge
r = position vector
Volt is the SI Unit of electric potential.
![]()
When unit work is done in moving a charge of one coulomb from infinity to a certain point due to an electric field against the electrostatic force, then electric potential is considered as 1 Volt electrostatic potential.
Conclusion
Electric charge is the fundamental physical property of matter because of which the matter experiences a force whenever it is kept in an electromagnetic field.
There are three types of electric charge which are as follows; positive electric charge, negative electric charge, and neutral.
The electric field in mathematical terms is defined as a vector field which can be associated or connected with each point in space.
The SI unit of electric charge is Coulomb.
The intensity of an electric field is a vector quantity that has magnitude as well as direction.
Formula for the intensity of electric field is ![]()
Volt is the SI Unit of electric potential.
![]()