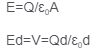
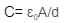

As charges accumulate on the plates, a charging current passes through the capacitor until the potential difference between the plates equalises the source potential. A parallel plate capacitor is defined as a device capable of storing electrostatic energy in the form of charge in the dielectric medium between the plates, and may therefore be compared to a rechargeable DC battery. If the working voltage of the capacitor exceeds the threshold voltage limit, a short circuit occurs between the plates due to dielectric breakdown, which occurs due to excessive heating of the dielectric medium caused by an increase in applied voltage beyond the limit, resulting in the capacitor rupturing.
Parallel Plate Capacitor
When two parallel plates are linked across a battery, an electric field is formed between them, and this configuration is known as a parallel plate capacitor.
The simplest type of capacitor is said to be a parallel plate capacitor, which is made up of two metal or metalized foil plates that are parallel to each other and are fixed by the surface area of the conductive plates and the separation distance between them. Before dielectric breakdown occurs, a parallel plate capacitor can only hold a certain amount of energy.
The parallel plate capacitor’s two plates are of identical size. They are linked to the power source. The plate receives a positive charge when it is attached to the battery’s positive terminal. The plate, on the other hand, which is linked to the negative terminal of the battery, develops a negative charge. Because of attraction force, charges trapped inside the capacitor plates.
Formula
Capacitance is the body’s capacity to hold an electric charge. Each capacitor has its own capacitance. Capacitance depends on the metallic plates of area A that is separated by d.
According to gauss law electric field is given by,
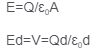
Where = medium permittivity, A = overlapping plate area, and d = distance separation between the plates.
As a result, we may change the capacitance of a parallel plate capacitor by adjusting the overlapping area, the distance between the plates, or by introducing a dielectric medium with a variable permittivity value.
Now to understand the concept of parallel capacitor we have to understand the concept of Dielectric.
Dielectric
A dielectric, is an insulator, or a particularly poor conductor of electric current When put in an electric field, dielectrics conduct almost minimal current because, unlike metals, they contain no loosely connected, or free, electrons that can drift through the material. Instead, electric polarisation takes place. Positive charges in the dielectric are displaced minutely in the direction of the electric field, whereas negative charges are displaced minutely in the opposite direction. This little charge separation, or polarisation, decreases the electric field within the dielectric.
Example
- Solid dielectric materials include ceramics, paper, mica, glass, and others.
- Distilled water, transformer oil, and other liquids are examples of Liquid dielectric medium.
- Nitrogen, dry air, helium, and different metal oxides are examples of dielectric gases.
Types of Dielectric
Dielectrics are classified based on the type of molecule found in the substance. Dielectrics are classified into two types: non-polar dielectrics and polar dielectrics.
Polar Dielectric: The dielectric in which the centre of mass of positive particles does not coincide with the centre of mass of negative particles is termed as Polar Dielectric. There’s a dipole moment present here. The molecules have an asymmetric form. When an electric field is applied, the molecules align with the electric field. When the electric field is removed and the net dipole moment in the molecules reaches zero, the random dipole moment is detected.
Example: H2O and HCl.
Non-Polar Dielectric: Within non-polar dielectrics, the centres of mass of positive and negative particles coincide. These molecules lack a dipole moment. These molecules have a symmetrical form. Examples: H2 , O2 , N2
Parallel Plate Capacitor Without Dielectrics
Parallel Plate Capacitor’s Capacitance

Conclusion
A parallel plate capacitor is a device capable of storing electrostatic energy in the form of charge in the dielectric medium between the plates, and may therefore be compared to a rechargeable DC battery. If the working voltage of the capacitor exceeds the threshold voltage limit, a short circuit occurs between the plates due to dielectric breakdown, which occurs due to excessive heating of the dielectric medium caused by an increase in applied voltage beyond the limit, resulting in the capacitor rupturing. The simplest type of capacitor is said to be a parallel plate capacitor, which is made up of two metal or metalized foil plates that are parallel to each other and are fixed by the surface area of the conductive plates and the separation distance between them.