At the origin of the fluid return process, interstitial fluid is the fluid present between the cells in all body tissues that enter the lymph capillaries. The fluids from the lymph are transported via gradually larger vessels in the lymphatic system through lymph nodes, where the tissues lymphocytes remove substances, and circulating lymphocytes are generally added to the lymph fluid. Lymphocytes are generally similar to blood plasma, the fluid component of blood.
Proteins add excess interstitial fluid to the bloodstream by the lymph. T lymph also transfers fats to the digestive system (beginning of the lacteals) via chylomicrons.
Now, what comprises the lymph? The lymph comprises tonsils, adenoids, spleen, and thymus.
Components of lymph
Components of lymph
The immediate environment of all cells is formed by the interstitial fluid. There is a ‘continuous movement of fluid through the arteriolar end of the semipermeable walls of capillaries into the interstitial fluid , to keep this environment and the supply of nutrients constant. Excess interstitial fluid and proteins are returned to the bloodstream by lymph. The major component of lymph is the fluid that resides between cells known as interstitial fluid. The fluid is mainly used to transfer substances, expel certain substances, and the white blood cells are allowed to access the interstitial spaces between cells to fight any foreign bacteria.
The lymph system also includes the:
- Tonsils
- Adenoids
- Spleen
- Thymus
Lymph nodes make the immune cells , which helps the body to fight infection and other complications caused by other foregin bodies. When bacteria are recognized in the lymph fluid, the lymph nodes make more infection-fighting white blood cells. Lymph fluids consist mainly of water, with various other substances present. The other components present are ions, organic materials, proteins, also the substances produced and excreted by the cells. What comprises the lymph other than interstitial fluid? Lymphocytes are cells that survive in the lymph and perform various functions for the body. Lymphocytes are a subgroup of white blood cells, which travel the whole body with the motive of looking after invading bacteria and other toxic substances.
The type of white blood cells present in the immune system of the majority of the vertebrates is lymphocytes. Lymphocytes also consist of natural killer cells, T cells, and B cells. They are named lymphocytes because they travel mainly within the lymph, using the ducts, tending to reach various day parts. The lymphocytes comprise natural killer cells, T cells, and B cells. The major component of the immune response in most animals is lymph. The majority of large animals like humans need to rely on lymph to serve various purposes.
Functions of lymph
The function of the lymphatic system is to carry lymph throughout the body. The lymphatic system is much similar to the circulatory system, consisting of lymphatic vessels similar to the veins and capillaries. The lymph nodes are connected to the vessels, where the lymph is filtered. The tonsils, spleen, and thymus are all lymphatic parts systems.
There are hundreds of lymph nodes in the human body. They are mostly located much deep inside the body, such as around the lungs and heart, or closer to the skin’s surface, such as the underarm or groin. What comprises the lymph for filtration? The largest lymphatic organ in our body is the spleen, located on the left side of the body just above the kidney. The spleen is also known as the blood filter; it controls the number of red blood cells and blood storage in the body and helps fight infection.
If any potentially dangerous bacteria, viruses, or other microorganisms in the blood are detected by the spleen and the lymph nodes, it immediately starts developing white blood cells called lymphocytes. The lymphocytes act as protectors against invaders by producing antibodies to kill the foreign microorganisms and stop the spread of infection.
Diseases caused in lymph
Large clusters of lymphatic cells found in the pharynx are tonsils. According to the study, tonsils are the body’s first defense mechanism. The tonsils sample viruses and bacteria which enter the body through the mouth or nasal cavity. But even the tonsils get affected by infectious viruses and become infected leading to a disease known as tonsillectomies.
Are you eager to know what the difference is between lymph vessels and blood vessels? Blood is a specialized body in organisms whose work is to transport oxygen and nutrients to several bodies and parts and also to carry away the waste products. Whereas, lymph is the clear fluid that flows through the lymphatic system and returns the excess interstitial fluid and proteins to the bloodstream. The blood flow in blood vessels is quite fast and in circulation and lymph flows slowly and in a single direction within the lymphatic system.
Blood vessels comprise calcium, proteins, and phosphorus, lymphatic vessels comprise lesser calcium, proteins, and phosphorus as compared to the blood vessels. Plasma leaves the body cells once its work is done delivering nutrients and removing debris.
Diseases and disorders of the lymphatic system are mainly treated by immunologists. However, vascular surgeons, dermatologists, oncologists, and physiatrists are also needed to get involved in the treatment of various lymphatic diseases and disorders.
Conclusion
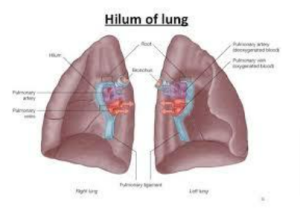
To summarize the abstract information we know about lymph, lymphocytes, and the lymphatic system, the lymphatic system plays a major role in providing the immune responses to foreign harmful microorganisms and various toxins that enter the body. Do you also know what is the hilar lymph node? And how does it play a role in our immune system?
Any lymph nodes that is present in the hilum or the triangular-shaped depression at the junction of each lung and its bronchi. Hilar lymph nodes collect lymph from the pulmonary nodes and drain the lymph to the tracheobronchial nodes. Hilar-interlobar 10 Hilar nodes are the proximal lobar nodes outside the mediastinal pleura and adjacent to the bronchus intermedius and mainstem bronchi.
They are inferior to the upper aspect of the upper lobe bronchi. The most common causes of bilateral hilar adenopathy include sarcoidosis and lymphoma.
Here is a labeled diagram of a hilar lymph node.