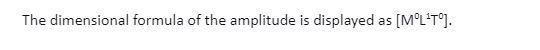
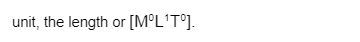
Introduction
The physical quantity’s dimensions are the powers to which the fundamental quantities are elevated to represent that amount. The physical quantity of the dimensional formula is an equation that explains how along with the base quantities contained in that amount. It is written by enclosing the symbols representing base amounts in square brackets with the corresponding power, i.e. [].
E.g., the Dimension formula of displacement is: [L].
A dimensional equation is obtained by equating a physical quantity with its dimensional formula, used to calculate the dimensional equation of any physical quantity.
In general, the total height of a wave is called its amplitude. According to physics, amplitude refers to the maximum dispersion of a point on a vibrating subject from its equilibrium point. As a result, the amplitude of a pendulum is one-half of the distance travelled by the bob as it moves from one side to the other. Vibrating sources produce waves, and their amplitude is proportional to the source’s amplitude.
Dimensional Formula of Amplitude
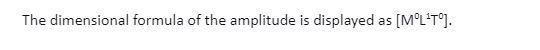
Where,
- M is called Mass.
- L is Length.
- T is called time.
The amplitude of a wave is the maximum displacement of the wave, which is nothing but the maximum displacement. And the dimensional formula for displacement is nothing but the fundamental unit, which is the length or [M0L1T0].
Angular speed:
The term “speed” is used in a variety of settings. For example, speed refers to how fast or slow an object moves. On the other hand, angular speed refers to how quickly something turns. In other words, it’s the change in an object’s angle per unit of time.
As a result, we’ll need to know the angular speed of the rotational motion to determine its speed. The angular speed formula transforms the distance travelled by a body in revolutions or rotations into time.
Furthermore, the radian is crucial in this context. When computing angular speed, we measure the angle in radians. When measuring angles in radians, the right angle is defined as 𝜋/2 radians. As a result, the total number of radians in a revolution will be roughly 6.28.
What is the Amplitude Formula?
Amplitude is also the largest deviation of a variable from its mean; hence the amplitude formula is derived. A is the symbol for amplitude. The displacement is denoted by, x = A sin (ωt+φ) or x = Acos (ωt+φ).
Here,
- x = displacement of wave (metre).
- A = amplitude.
- ω = angular frequency (rad/s).
- t = time period.
- φ = phase angle.
The average of the sine or cosine function’s maximum and minimum values are also known as the formula of amplitude.
Energy transported related to the amplitude:
Amplitude is the quantity of energy carried by the wave and is proportional to its energy. Large amplitude occurs when there is a high energy, while small amplitude occurs when there is low energy. The amplitude of a wave, as previously stated, refers to the maximum amount of displacement a particle on the medium can undergo from its resting position.
The following is the rationale behind the energy-amplitude relationship: When a slinky is stretched out horizontally and a transverse pulse is applied, the first coil receives an initial displacement amount. The displacement is caused by an individual exerting effort on the loop to move it a certain distance from rest.
The more energy a person devotes to the pulse, the more work they will transfer to the first coil. The more work performed on the first coil, the more significant displacement it receives. The more displacement the first coil receives, the more amplitude it will have. Finally, the amplitude of a transverse pulse is proportional to the amount of energy it carries across the medium. Putting a lot of energy into a transverse pulse does not affect the pulse’s wavelength, frequency, or speed.
Importance of Amplitude
With the help of a test particle, the amplitude effect has been examined thoroughly. A simple two-wave model has been used to reflect the recently found amplitude modulation of a whistler wave field. We study the impact of different modulation frequencies on nonlinear interactions by altering the frequency separation between the two waves.
When the resonance overlap requirement is met, the following change in electron pitch angle and energy may differ significantly from what ideal single-wave nonlinear models predict. We get the probability distribution of distinct sorts of electron responses by using a previously discovered probability distribution of the subpacket modulation frequency of a chorus event.
The observed subpacket distribution induces particle responses in both non-overlapping and overlapping regimes. The findings show that the observed amplitude modulation should be considered when quantifying interactions between electrons and recently detected large-amplitude whistler waves of chorus waves.
Conclusion
Dimensional Formula of Amplitude
Amplitude:
As the maximum displacement of the wave, the amplitude wave is nothing but the maximum displacement. And the dimensional formula for displacement is nothing but the fundamental
Angular Speed:
The angular speed is the rate at which an object or item rotates. Angular momentum refers to how quickly something turns. In other words, it’s the change in an object’s angle per unit of time.
Dimensional Formula:
The dimensional formula of any quantity is the statement expressing the powers to which the fundamental units must be increased to obtain one unit of a derived quantity.